Climate Education Hub
Learn about climate science, common misconceptions, and the latest research
Greenhouse Effect Discovered
Joseph Fourier describes the Earth's natural "greenhouse effect"
Human-Caused Warming
Guy Callendar links CO₂ increases from human activities to warming
CO₂ Monitoring Begins
Charles David Keeling begins measuring atmospheric CO₂ at Mauna Loa
IPCC Established
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change is formed
Earth Summit
UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is adopted
Kyoto Protocol
First international agreement to reduce greenhouse gases
Paris Agreement
Global agreement to limit warming to well below 2°C
IPCC Special Report
Report on impacts of global warming of 1.5°C
COP26
Glasgow Climate Pact accelerates action on climate change
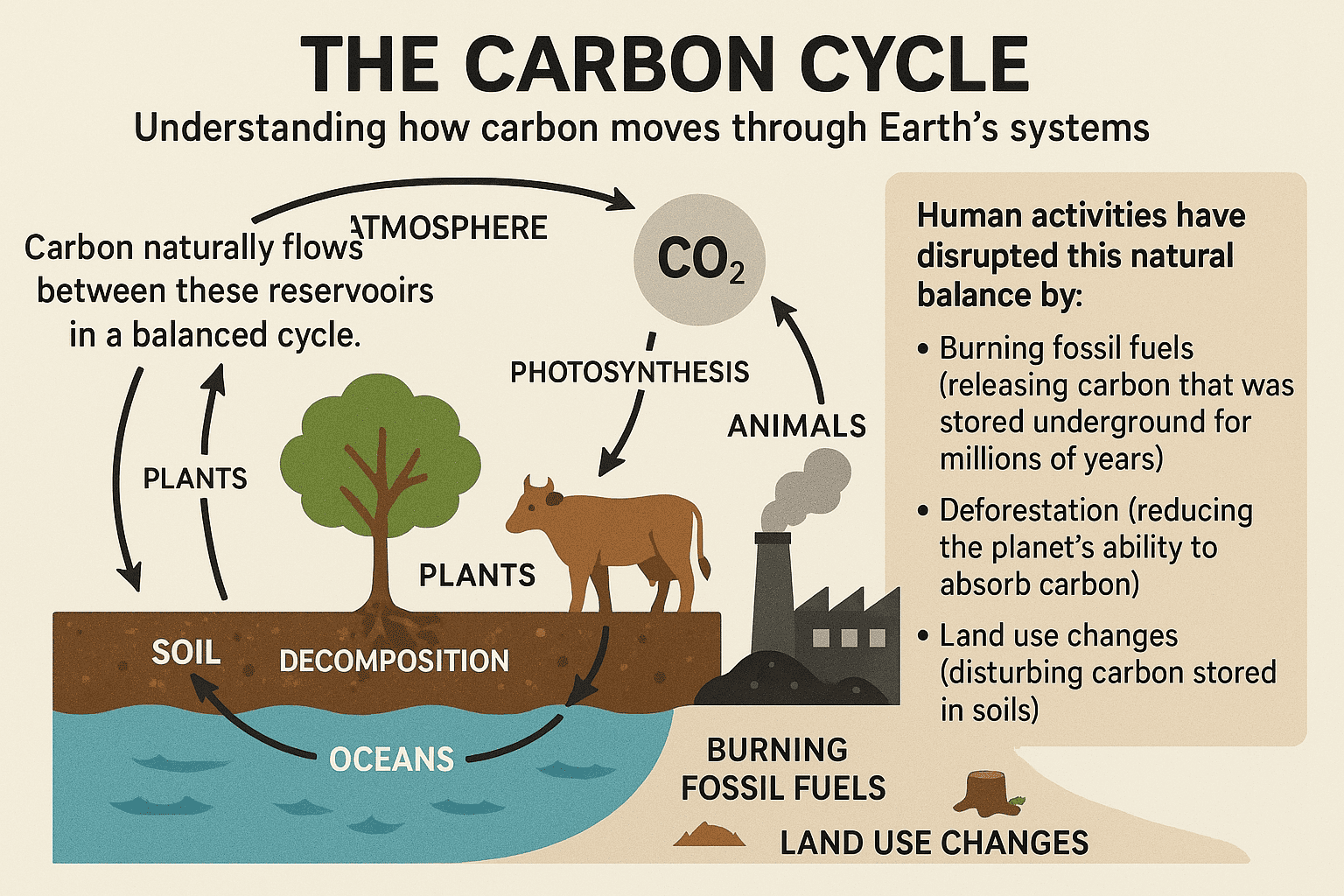
The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves between different reservoirs on Earth, including the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and fossil fuels.
soil, plants, and fossil fuels.
Carbon naturally flows between these reservoirs in a balanced cycle. Plants absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis, animals consume plants and release CO₂ through respiration, and when organisms die, carbon returns to the soil and oceans.
Human activities have disrupted this natural balance by:
- Burning fossil fuels (releasing carbon that was stored underground for millions of years)
- Deforestation (reducing the planet's ability to absorb carbon)
- Land use changes (disturbing carbon stored in soils)
Carbon Cycle Infographic